
Feasibility and acceptability of Narrative Exposure Therapy to treat individuals with PTSD who are homeless or vulnerably housed: A pilot randomized controlled trial
This study had two goals. Since this treatment has never been used in homeless or vulnerably housed populations before, our first goal was to determine whether it was possible to recruit patients from this under-represented population to participate in a clinical trial that focused on trauma. Our second goal was to learn if both NET and completing a family history was acceptable to the patients enrolled in the study.

Interventions to treat post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in vulnerably housed populations and trauma-informed care: A scoping review
A trauma-informed care approach to care acknowledges that we need a complete picture of a person’s life (both past and present) to be able to provide healthcare that is focused on healing. The Trauma-Informed Care Implementation Resource Center explain that this approach understands that the impacts of trauma are widespread looks to identify signs and symptoms of this in patients, family, and staff; use knowledge about trauma to inform an organization’s policies and procedures; and, actively avoid re-traumatizing individuals.

Innovations in Suicide Assessment and Prevention During Pandemics
Research suggests that during previous pandemics, there was an increase in suicide risk as well as suicide-related behaviours. Given this, it is expected that we will see the same increase during the COVID-19 pandemic. Research has also found that specific groups at at higher risk than others, including older adults, especially older women; those who are unemployed or under-employed; those with pre-existing mental health disorders and/or substance misuse; and, frontline and social service workers.

Needs, gaps and opportunities for standard and e-mental health care among at-risk populations in the Asia Pacific in the context of COVID-19: A rapid scoping review
In March 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) a global pandemic. It is expected that this will have a major impact on people’s mental health. Because of the pandemic, many providers have had to switch to virtual tools to deliver care. As such, we have to consider what equitable access to these virtual tools looks like for patients that are most at risk of having mental health problems.

Strategies for facilitating the delivery of cluster randomized trials in hospitals: A study informed by the CFIR-ERIC matching tool
Cluster randomized trials (CRTs) are valuable tools for evaluating interventions in hospital settings, but their successful implementation can be challenging. This study aimed to identify strategies for facilitating the delivery of CRTs in hospitals, utilizing the CFIR-ERIC matching tool.
By employing a comprehensive approach, the study examined existing literature and integrated the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR) and the Expert Recommendations for Implementing Change (ERIC) matching tool. This combined framework provided a systematic approach to identify strategies that align with the specific contextual factors influencing CRT implementation in hospitals.
The BEACON Study: Protocol for a Cohort Study as Part of an Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Smartphone-Assisted Problem-Solving Therapy in Men
Attending the emergency department for an episode of self-harm is strongly associated with death by suicide in the next year. There is evidence to suggest that men may be especially at risk, accounting for almost 2/3 of suicide deaths in Ontario.
To address this, we have developed an blended intervention that includes face-to-face problem-solving therapy as well as a smartphone app and clinician dashboard treatment package. The clinician dashboard allows a therapist to push out targeted content and resources to their patients and the smartphone application allows the patient to connect with their therapist in between sessions as well as access resources designed to manage thoughts of self-harm and suicide.

The Impact of Infectious Disease-Related Public Health Emergencies on Suicide, Suicidal Behavior, and Suicidal Thoughts: A Systematic Review
Public health crises and epidemics, like the COVID-19 pandemic, have the potential of increasing suicide risk in the communities affected. To appropriately respond to these crises, we need high quality research evidence. We conducted a systematic review of prominent databases to evaluate the current state of research about public health crises and suicide-related outcomes.

Coach-Facilitated Web-Based Therapy Compared With Information About Web-Based Resources in Patients Referred to Secondary Mental Health Care for Depression: Randomized Controlled Trial
Depression is a common mental disorder that has a significant impact on quality of life as well as a high social burden. Many of those with depression go on to self-harm or die by suicide. Due to long wait times for face-to-face therapy, treatment is often limited to drug therapies despite recommendations that counselling should be a first-line treatment for those with mild to moderate levels of depression.
To address this, we conducted a clinic trial to test the efficacy of combining online therapy program for depression (The Journal) with the use of a telephone coach.

Barriers and enablers to conducting cluster randomized control trials in hospitals: A theory-informed scoping review
Cluster randomized control trials (CRCTs) are essential for evaluating interventions in hospital settings, but their implementation can be complex. This study aimed to identify the barriers and enablers to conducting CRCTs in hospitals through a theory-informed scoping review.
By systematically examining existing literature, the study identified key factors that hinder or facilitate the successful implementation of CRCTs in hospital settings.
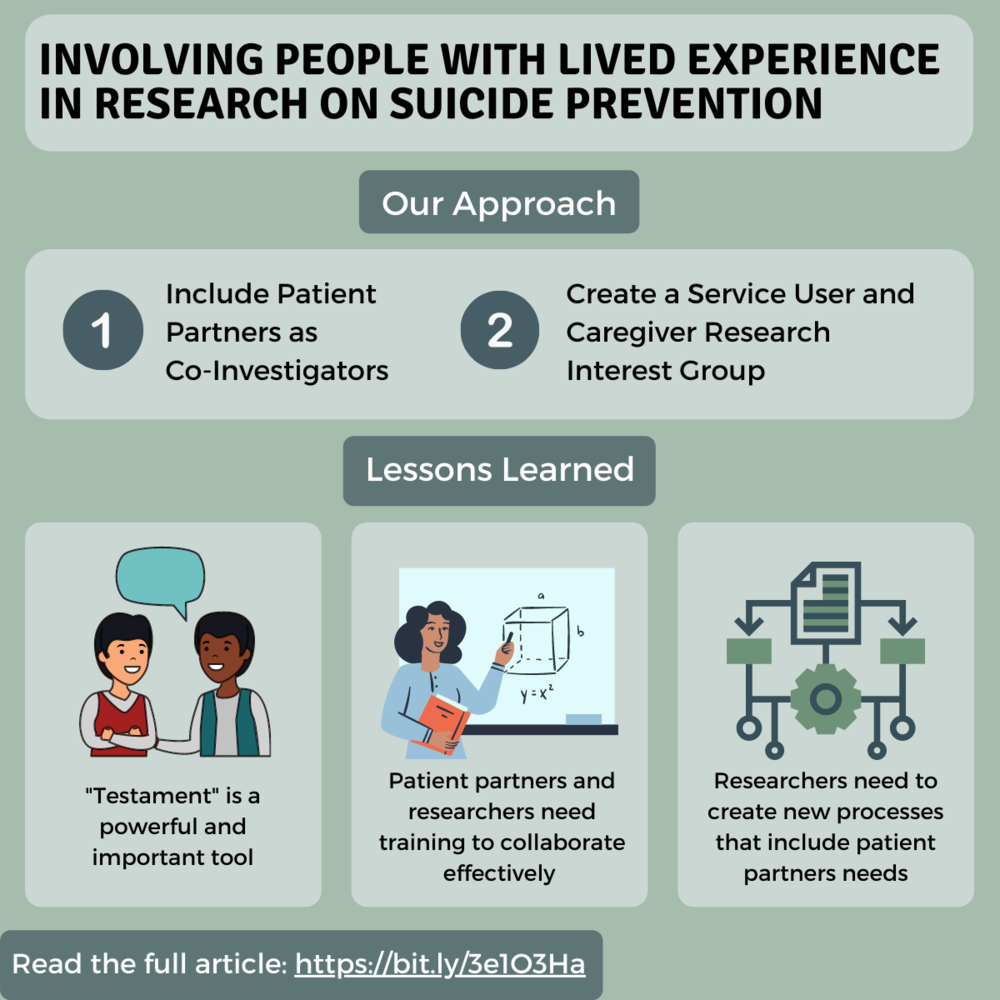
Involving People with Lived Experience in Research on Suicide Prevention
Suicide is one of the leading causes of death in Canada, with about 10 Canadians dying by suicide each day. Men represent nearly two-thirds of those who die by suicide after an initial episode of self-harm. However, interventions for these men have had modest effects and, generally, suffer from a lack of engagement by patients. Partnerships with patients and other people with lived experience of suicide are essential to developing interventions that work for the people they are designed to treat. One of the key goals of The BEACON Study is to develop patient partnerships to inform both what intervention we developed and how to best recruit participants in the emergency department following an episode of self-harm. This article describes our experience with engaging patient partners and the key lessons we have learned so far.
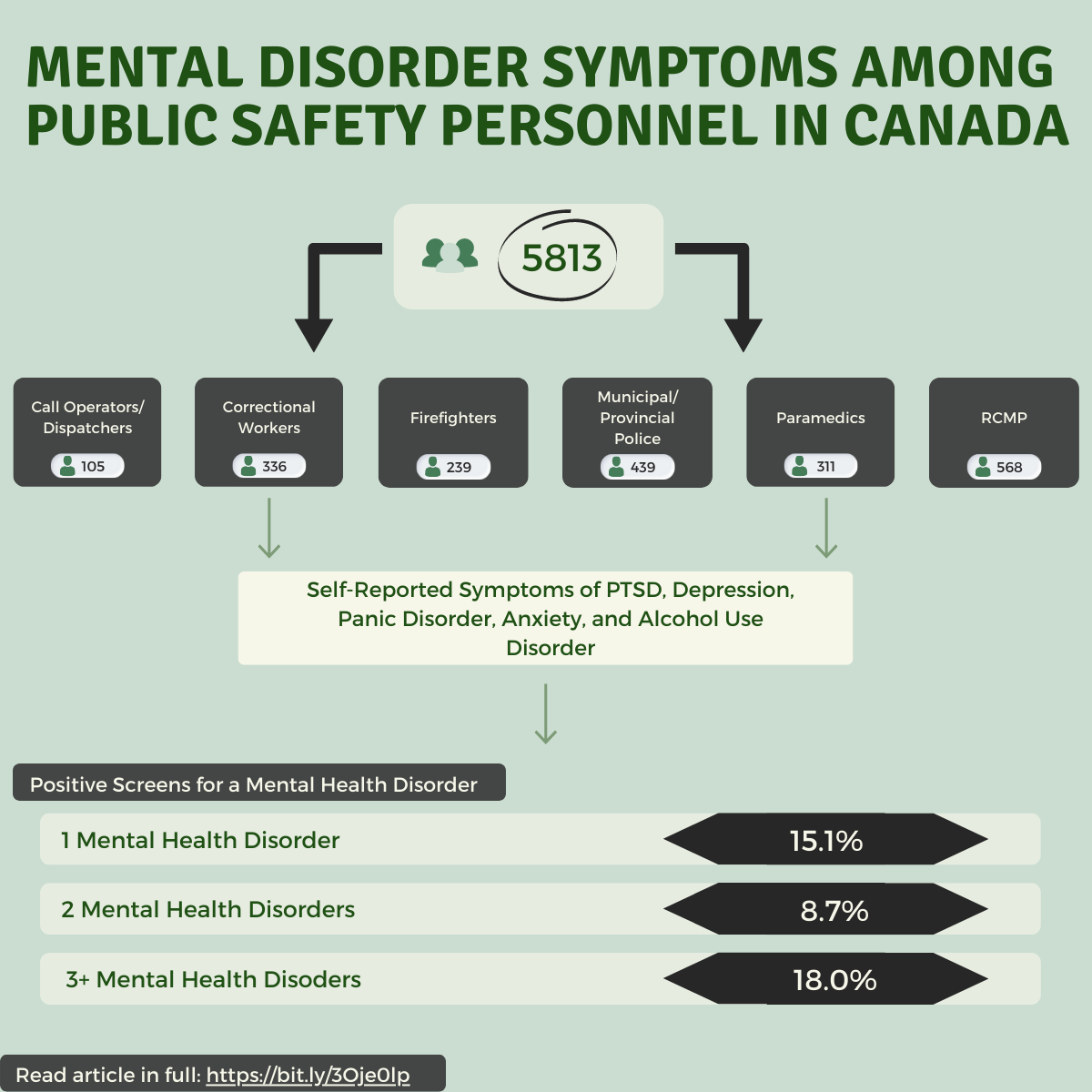
Mental disorder symptoms among Public Safety Personnel in Canada
Because of their jobs, Canadian Public Safety Personnel (PSP) are often exposed to situations that are potentially traumatizing. Exposure to these situations put PSP at a higher risk of developing mental health disorders, such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression, anxiety, panic disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and substance use disorders. Prior to this study, data on the rates of mental health disorders among Canadian PSP were extremely limited.
To address this, we conducted an online survey that asked questions about mental health symptoms among PSP across Canada